The evolution of fabric technology is more important than ever as industries face rapidly changing demands. From architecture and engineering to manufacturing and innovation, emerging industries require adaptable and sustainable fabric solutions to meet the challenges of today and tomorrow. This blog explores the role of advanced textiles, particularly focusing on how they adapt to serve a wide range of modern applications.
Why Fabric Innovation Is Essential
Fabric solutions once exclusively related to clothing and upholstery are now the backbone of various industrial applications. Whether it be in the automotive sector, construction, or healthcare, fabric innovation plays a key role in delivering strength, flexibility, and sustainability.
Here are a few strong reasons the industry is experiencing a shift towards cutting-edge fabric solutions:
- Rising Demand for Durability
Industries such as automotive and engineering require highly durable materials that can withstand wear and tear while delivering long-lasting performance. For example, industrial fabrics used in car interiors or machinery covers must hold up against frequent use and exposure to a variety of elements.
- Focus on Lightweight Solutions
Lightweight materials are paramount, especially in applications that prioritize efficiency and energy savings, like aerospace and transport industries. Innovative fabric technologies are stepping up to reduce the weight of existing material solutions while maintaining structural integrity.
- Sustainability Concerns
With sustainability being a top priority across all sectors, the shift toward eco-friendly and biodegradable materials is driving fabric innovation. Non-woven textiles are one example of a sustainable solution that reduces waste while supporting high-performance applications.
Categories of Industrial Fabric Solutions
Emerging industries are utilizing advanced fabric technologies for customized solutions, often tailored for specific applications. Below are some key categories of industrial fabric solutions being developed to align with industry needs effectively:
1. Technical Textiles
These are engineered for functionality rather than aesthetics. They are commonly used for applications such as insulation, weather resistance, and safety in fields like construction and healthcare. The use of technical fabrics in protective clothing, for instance, ensures high performance in harsh conditions.
2. Non-Woven Textiles
Non-woven fabrics are defined by their unique production process, which binds fibers together mechanically or chemically without weaving. Used extensively across medical, automotive, and filtration industries, non-woven textiles provide cost-effective and sustainable fabric options. By partnering with a non-woven textile manufacturer, industries can gain access to high-quality materials tailored to specific needs.
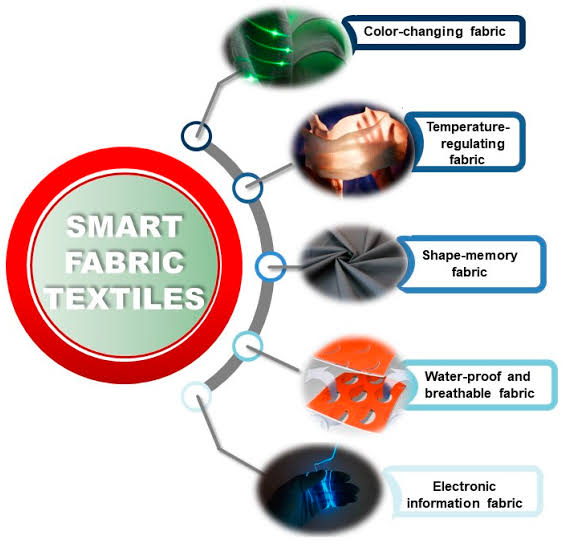
3. Smart Textiles
Innovations in smart textiles, such as conductive fabrics and sensor-integrated materials, are transforming how industries gather and analyze data. These fabrics are particularly relevant for wearable tech, healthcare monitoring solutions, and industrial efficiency tracking.
4. Coated Fabrics
Coated fabrics are textiles with protective or performance-enhancing coatings. These coatings can provide water resistance, fire retardation, or UV protection. Coated fabrics are frequently utilized in construction projects and outdoor installations, such as outdoor canopies or industrial tents.
Industry Needs Driving Modern Textile Innovation
Industries approach fabric solutions with unique functional requirements. Below, we break down the emerging needs across four diverse industries:
1. Architecture
Architects increasingly require lightweight, flexible, and visually striking fabric materials for modern buildings and installations. Applications such as tensile structures, roofing, and acoustical panels call for technical textiles that integrate strength with aesthetic appeal.
For example, in stadium designs or airport terminals, the use of durable, weather-resistant tensile membrane structures is rapidly gaining popularity. It’s critical for fabric manufacturers to focus on weatherproofing and solar reflectivity while ensuring cost-efficiency.
2. Engineering
Engineers rely on materials with exceptional tensile strength, thermal resistance, and adaptability for use in complex mechanical systems. From industrial tarps in manufacturing to conveyor belts in logistics, fabric engineering forms the base of crucial applications.
The demand for precision tailoring has also risen, as engineers require bespoke solutions to meet size and durability needs in very specific settings.
3. Manufacturing
Automation and demand for lean production processes in industrial manufacturing have led to an increasing dependence on advanced fabric systems. Durable conveyor fabrics that maintain smooth operation and filtration textiles for pollutants are two examples of how innovation is transforming manufacturing.
Non-woven textiles are also a crucial element in modern manufacturing processes due to their lightweight nature and structural adaptability.
4. Innovators and Product Designers
For innovators, fabric innovation plays a vital part in product research and design. Customization capabilities in textiles now allow unconventional materials to be applied to applications as diverse as 3D printing bases, wearables, and even food grade wrappers.
Innovation leaders often experiment with combinations of technical textiles and smart fabrics in order to create breakthroughs that satisfy today’s fast-paced consumer needs.
Integrating Sustainability into Emerging Fabric Solutions
The industry’s move toward sustainable practices is reshaping the landscape of textile innovation. Here are just a few strategies driving this change:
- Recycled Materials – The integration of recycled fibers and textiles into industrial manufacturing reduces environmental impact while providing durable materials for products.
- Eco-friendly Processes – Non-woven textiles, known for reducing waste during production, address both durable performance and sustainability goals.
- Biodegradable Alternatives – Bio-textiles are a growing segment of the fabric industry, providing solutions that naturally break down in the environment.
Meeting the Challenges of Tomorrow
Advanced textile solutions are shaping the industries of tomorrow. From enabling lighter, more durable construction projects to revolutionizing products with embedded technology, innovation in fabric manufacturing continues to play a fundamental role across sectors.
Staying informed and connected with industry experts—whether in architecture, engineering, or manufacturing—is key to staying ahead of this evolution. With non-woven fabrics, technical textiles, and smart fabrics becoming critical components of success, adaptability and innovation will for